Practicals
Video Clips
Quiz Time
Saturday, January 19, 2013
Friday, January 18, 2013
Unit 02 - Chemical and cellular basis of life
Unit-2
Chemical and cellular basis of life
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=cFX4JrsPaUshttp://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=37Eyq6K0GPg

Hirarchical organization of living systems
Cell Theory
http://orion.chemi.muni.cz/e_learning/=Animace/11-Lipidy/10-2a_FluidMosaic/FluidMosaic.htm

http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=Qqsf_UJcfBc

http://www.goldiesroom.org/Note%20Packets/06%20Transport/00%20Transport--WHOLE.htm
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=moPJkCbKjBs
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=C7XliJVJhok
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=C7XliJVJhok


http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=QGAm6hMysTA


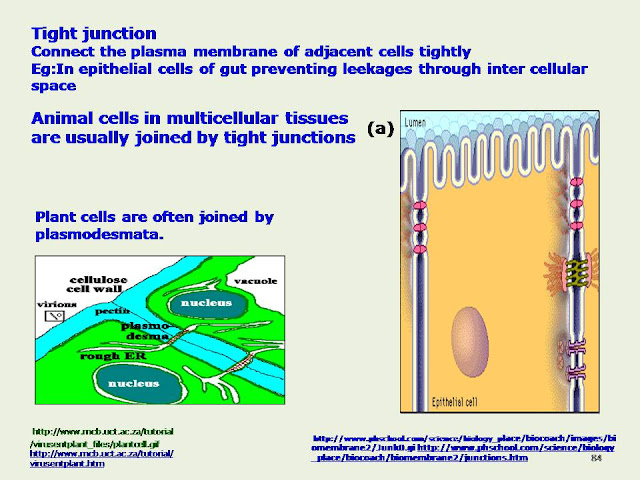
Cells and tissues contribute to the functioning of organisms
In multi cellular organisms , the cells are organized into tissues , organs and organo systems
Tissue is a group of physically linked cells with common origin specialized for a paticular function or functions
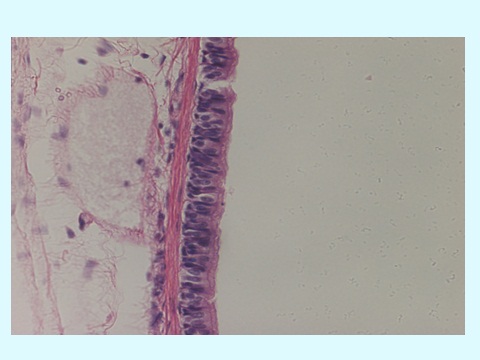
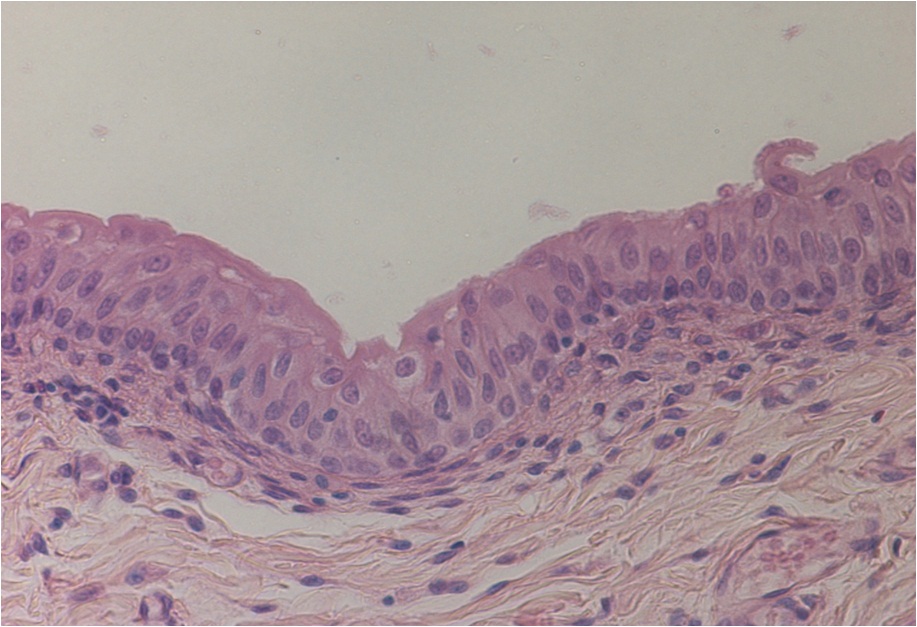
Animal Tissues
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue
Cartilege
Bones
Blood









Muscle Tissue

Nervous Tissue





The process of cell division
Cell division results a genetically identical daughter cells
Interphase
This is a period of intense synthesis and growth in the cell. The cell produces many materials required for its own growth and activities. The genetic material DNA replicates during interphase.
Cytokinesis
It is the process of division of the cytoplasm to result in the formation of daughter cells.
Cell Cycle
The length of the cycle depends on the nature of cell and various external factors like temperature food and oxygen availability. Bacterial cells may divide every 20 minutes, epithelial cells living the small intestine divide once in 8 to 10 hours, onion root tip cells take about 20 hours to divide. Some specialised cells like the nerve cells never divide.

Cytokinesis
It is the division of the cytoplasm
In animals


- A cleavage furrow appears at the begining of Telophase
- The furrow deepens as spindle breaks down
- The ingrowing constrictions join and seperate two daughter cells
In plants
- There is a formation of cell plate between two daughter cells
- This grows from the middle towards the peryphery and finnaly joins the cell wall
- The cell plate represents the middle lamella between the walls of two adajacent cells
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj9nTLp5TGtw0DGk4bcREXo_Usb0i6TiTt-eOxVPe_hMn3pypds56EK5h4bZQUwv6MM2MzIR3LntoTW_M6oQ4ag2SOJOP6dkAXm70O0-HGMFOcb6LHlpyjr7X5sB0QKON2SYIWBw8rC5DQ/s1600/cytokinensis+in+animals.jpg
Meosis
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=Q6ucKWIIFmg
http://cdn.c.photoshelter.com/img-get/I0000jWtxX4TCrgs/s/860/860/Fphoto-64720907B-6WRc.jpg
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=4B071d9Ywbc
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=cvlpmmvB_m4
Prophase ProphaseI
- Homologous chromosoms do not pair Homologous chromosoms pair
Synapsis and crossing over
- Individual homologues align Paired homologous
on metaphase plate
Sister chromatids separate Homologous chromosomes
chromatids remain together
and two cells result,
Meiosis II
Each containing
Chromosomes align,
the original number Sister chromatids seperate
of chromosomes and four haploid cells result,
Each containing half the
original number of homologues
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=ZkJMVxafyoU
Significance of mitosis
It keeps the chromosome numberconstant and genetic stability in daughter cells.
It helps in growth and develpoment of zygote into adult through embryo formation
It provides new cells for repair and generation of lost parts and healing of wounds
It helps in sexual reproduction
Significance of meiosis
It maintains a constant number of chromosomes by producing haploid gametes.
Due to crossing over in meiosis , organisms may exchange genes and cause genetic variations in species.This variations serve the raw material of evolutionary process.
Chromosomal and genomic variations are the sources of useful variations.
http://www.biologyexams4u.com/2012/09/difference-between-mitosis-and-meiosis.html#.UTMGhaKLDfI
The energy relationship to metabolic process
http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/9834092339/student_view0/chapter6/how_enzymes_work.html
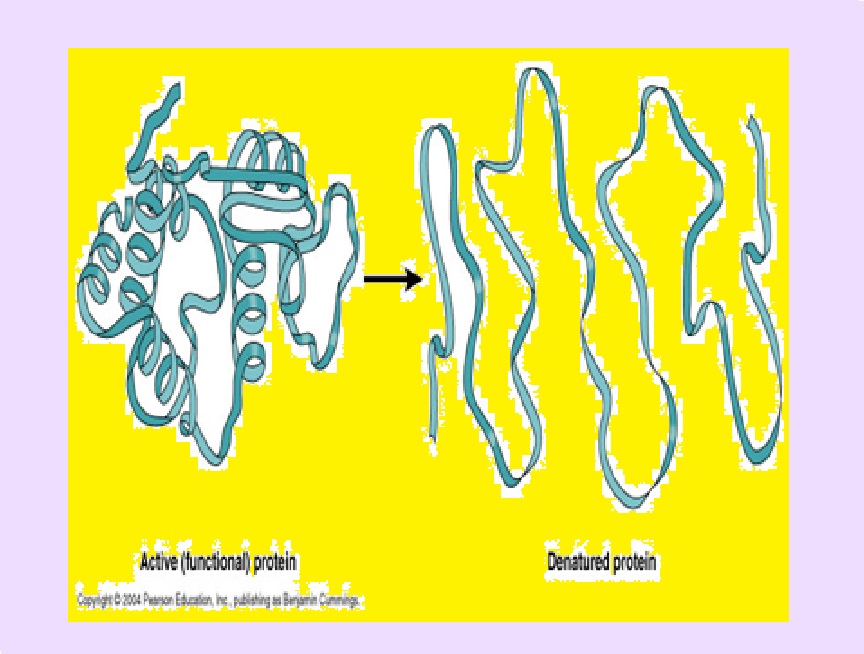
Enzymes are specific, combined with substrates to form enzyme- substrate complexes through active sites
http://www.rsc.org/Education/Teachers/Resources/cfb/enzymes.htm
http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/9834092339/student_view0/chapter8/photosynthetic_electron_transport_and_atp_synthesis.html
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0070960526/student_view0/chapter5/animation_quiz_1.html
http://www.biologycorner.com/APbiology/cellular/notes_photosynthesis1.html
Light reaction Calvin cycle reaction
http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/cellresp/review2.html

Total theoretical yield of ATP in eukaryotes is 36.

http://webclass.angelo.edu/biology/Scenarios/StudyGuides/UnderSea/UnderSeaset.html
http://www.mhhe.com/cgi-bin/netquiz_get.pl?qfooter=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/maderinquiry9/student/olc/art_quizzes/0154fq.htm&afooter=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/maderinquiry9/student/olc/art_quizzes/0154fa.htm&test=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/maderinquiry9/student/olc/art_quizzes/0154q.txt&answers=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/maderinquiry9/student/olc/art_quizzes/0154a.txt
http://webclass.angelo.edu/biology/Scenarios/StudyGuides/UnderSea/UnderSeaset.html
Significance of mitosis
It keeps the chromosome numberconstant and genetic stability in daughter cells.
It helps in growth and develpoment of zygote into adult through embryo formation
It provides new cells for repair and generation of lost parts and healing of wounds
It helps in sexual reproduction
Significance of meiosis
It maintains a constant number of chromosomes by producing haploid gametes.
Due to crossing over in meiosis , organisms may exchange genes and cause genetic variations in species.This variations serve the raw material of evolutionary process.
Chromosomal and genomic variations are the sources of useful variations.
http://www.biologyexams4u.com/2012/09/difference-between-mitosis-and-meiosis.html#.UTMGhaKLDfI
The energy relationship to metabolic process
The role of enzymes in regulating metabolic reactions
Enzyme combines with substrates to form short lived enzyme- substrate complexes.
Within this complex reactions between enzyme and substrate take place.
Once the reaction is completed complex breaks up to products and
enzymes .
Enzymes remain unchanged and is free to react with new substrate
Enzymes are specific, combined with substrates to form enzyme- substrate complexes through active sites
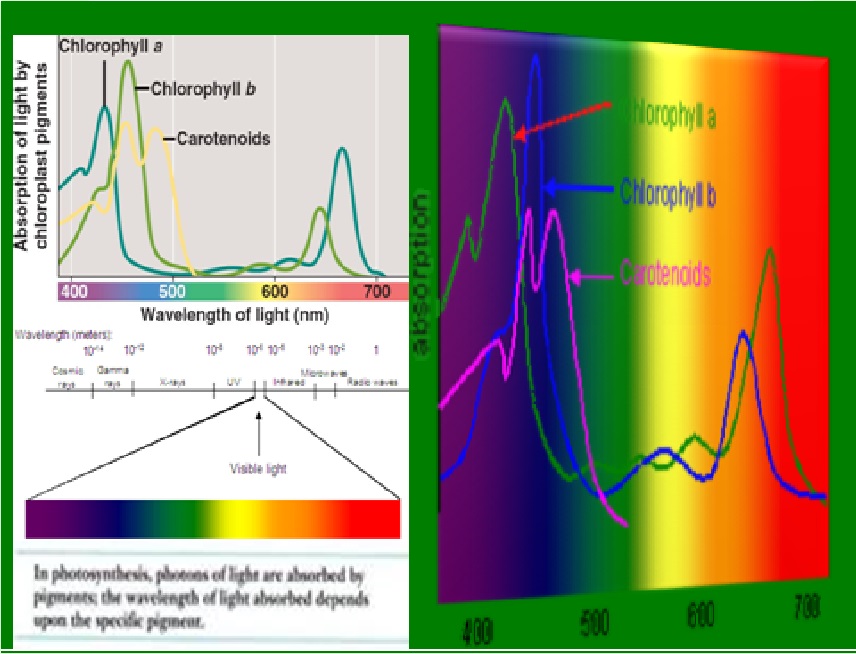
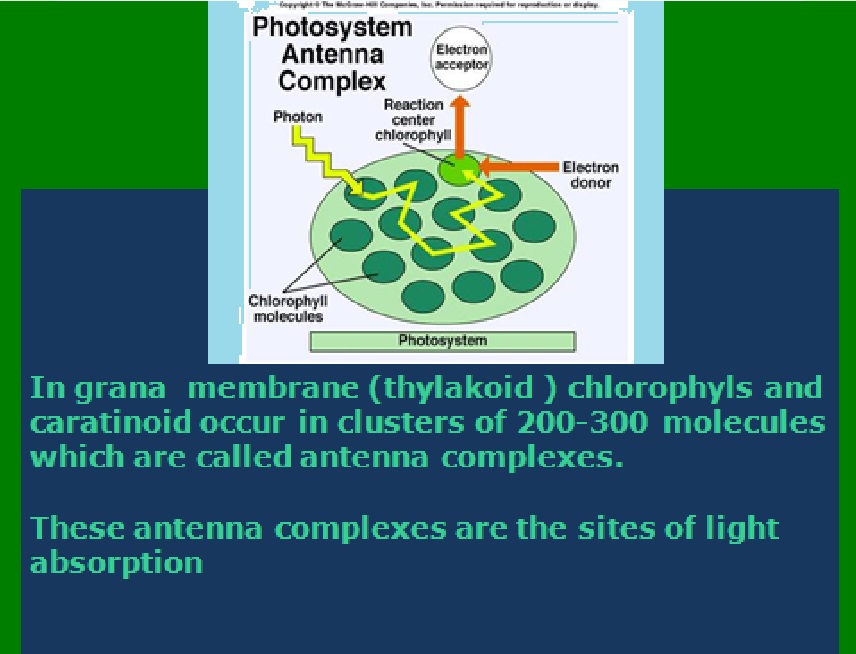
Photosynthesis as an energy fixing mechanism
Visible light is a very small pottion of the electro magnetic spectrum.Photosynthetic organisms use some of the wavelengths of visible light to provode energy for food production
http://faculty.southwest.tn.edu/rburkett/GB-1%20photosynthesis.htm
Overview of C3 photosynthesis
Calvin Cycle
http://mandevillehigh.stpsb.org/teachersites/laura_decker/calvin_cycle.htm
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0070960526/student_view0/chapter5/animation_quiz_1.html
http://www.biologycorner.com/APbiology/cellular/notes_photosynthesis1.html
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/images/photosyn_1.gif
Leaf anatomy of C3 plant Leaf anatomy of C4 plant
C3 plants only have C4 plants show different
mesophyl cells anatomical features /
circle of bundle sheath
cells around vascular
bundles in leaves
Water and oxygen cycle between chloroplasts and mitochondria within a plant cell, as do glucose and carbon dioxide . Cells with chloroplast require an outside source of carbon dioxide and water and generate glucose and oxygen. Cells without chloroplasts, such as animal cells, require an outside source of glucose and oxygen and generate carbon dioxide and water
Cellular respiration as a process of obtaining energy
It is not necessary to memorize these steps, but an understanding of each process is necessary in order to understand normal physiology and abnormal conditions that may interfere with respiration and possibly lead to death.
Note the role of NAD as a hydrogen acceptor (carrier), and note how many molecules of NAD and FAD are used. What eventually happens to the hydrogen that is passed to NAD and FAD?
The last half of glycolysis, where a net gain of two ATPs occurs.
When oxygen levels are not sufficient, pyruvate is converted into lactate in our muscles by the use of the enzyme LDH. Yeasts have different enzymes, and convert pyruvate into ethyl alcohol, a process utilized in brewing. Note that no more energy (ATP) is obtained by these processes.
Glucose, proteins, and lipids may be processed into Acetyl Co-A.
Various amino acids may be converted into the molecules found within the KCAC, and may be utilized as fuel.
The beginning of the Krebs cycle, in which the first two CO2s are produced.
Remember that for each molecule of glucose, two Acetyl Co-A molecules are produced; therefore the KCAC occurs twice for each glucose, so all products here are X 2..
The ETS uses Cytochoromes, iron containing pigments, each of which has a slightly higher electronegativity than the previous one used; this allows hydrogen electrons and ions to gradually be passed to the final step, which is the combination of hydrogen and oxygen, to produce water. Note that 6 molecules of water enter into the reactions at various steps, and that 12 molecules are produced in the end. The original simplified formula is sometimes shown with 6 additional water molecules on each side of the equation.
http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/cellresp/review3.html
The ETS occurs within the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
Both deamination and beta-oxidation occur within the liver, thus allowing use of proteins and lipids as fuels.
In the absence of oxygen in yeasts, two molecules of ethyl alcohol plus one molecule of CO2 are produced from each molecule of glucose.

http://www.mhhe.com/cgi-bin/netquiz_get.pl?qfooter=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/maderinquiry9/student/olc/art_quizzes/0154fq.htm&afooter=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/maderinquiry9/student/olc/art_quizzes/0154fa.htm&test=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/maderinquiry9/student/olc/art_quizzes/0154q.txt&answers=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/maderinquiry9/student/olc/art_quizzes/0154a.txt
http://webclass.angelo.edu/biology/Scenarios/StudyGuides/UnderSea/UnderSeaset.html
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)